Typically, De novo Lipogenesis refers to the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, which is the beginning of de novo lipogenesis. Malonyl-CoA (3 carbons) is first created by removing acetyl-CoA from the mitochondria. An acetyl-CoA-malonic acid complex is produced when malonyl-CoA is combined with another acetyl-CoA. A 16-carbon fatty acid is formed by adding 2 carbons to carbons through a similar process 7 times.

Triglycerides are stored as a large portion of the fatty acids synthesized.
A de novo synthesis of fatty acid involves the production of palmitate from acetyl CoA through a series of reactions.
Here, De Novo is the word that actually means a new way to synthesis something. In this sector, we are dealing with synthesis of fatty acids especially – palmitic acid.
For processing the De Novo synthesis of fatty acids, i.e., palmitic acid, there are three sites where this synthesis takes place majorly. These sites are given below as -
Reactions of fatty acids synthase complex



There are 16 carbon atoms in palmitate, and 2 of these atoms come from Acetyl CoA, and the remaining 14 atoms come from Malonyl CoA. The overall reaction between palmitate and the body is summarized as follows:

A de novo synthesis of fatty acid involves the production of palmitate from acetyl CoA through a series of reactions.
Here, De Novo is the word that actually means a new way to synthesis something. In this sector, we are dealing with synthesis of fatty acids especially – palmitic acid.
For processing the De Novo synthesis of fatty acids, i.e., palmitic acid, there are three sites where this synthesis takes place majorly. These sites are given below as -
- Adipose tissue
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Production of NADPH and acetyl CoA
- Conversion to malonyl CoA from acetyl CoA
- Reactions of fatty acids synthase complex
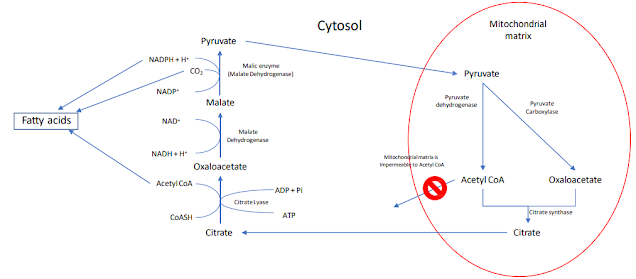
- For fatty acids to be produced, acetyl CoA is essential. The main source of Acetyl CoA is pyruvate, which is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix, as well as amino acids and ketone bodies.
- To transport acetyl CoA, alternative arrangements must be made because it cannot penetrate mitochondrial membranes.
- Oxaloacetate is formed from acetyl CoA, which is then condensed to acetyl CoA. Citrate is easily removed from the matrix and transported into the mitochondrial cytosol matrix
- During the fermentation process, citrate is formed by combining enzymes and fatty acids.
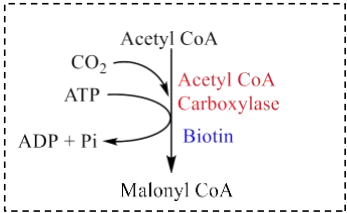
- Malonyl CoA is produced by carboxylation acetyl CoA.
- Biotin is required for CO2 fixation in this ATP-dependent reaction.
Reactions of fatty acids synthase complex
- A multifunctional enzyme called the fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex catalyzes the reactions of fatty acid synthase.
- ACPs (acyl carrier proteins) and enzymes are both present in each monomer.
- Following is a discussion of this sequence of reactions.
There are 16 carbon atoms in palmitate, and 2 of these atoms come from Acetyl CoA, and the remaining 14 atoms come from Malonyl CoA. The overall reaction between palmitate and the body is summarized as follows:
Get subject wise printable pdf notesView Here



No comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't spam. Comments having links would not be published.